Table of Contents >> Show >> Hide
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain that plays a critical role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle. Often referred to as the “sleep hormone,” melatonin is available in supplement form and is commonly used by people seeking to improve their sleep quality or alleviate insomnia. Alcohol, on the other hand, is a commonly consumed substance known for its relaxing effects and its ability to impair cognitive and motor functions. But what happens when melatonin and alcohol are combined? In this article, we’ll explore the interactions between melatonin and alcohol, examine the functions of melatonin in the body, and discuss its various uses in both medical and wellness contexts.
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the pineal gland, a small gland located deep within the brain. It helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, which is the internal clock that dictates our sleep-wake cycle. The production of melatonin is closely tied to light exposure. It increases as it gets darker, signaling to the body that it’s time to prepare for sleep. Conversely, it decreases when exposed to light, helping us wake up in the morning. This hormonal balance is key to maintaining a healthy sleep schedule and promoting restful sleep.
In addition to its well-known sleep-inducing properties, melatonin has antioxidant effects and plays a role in the immune system and hormonal regulation. However, its most commonly discussed benefit is its ability to regulate sleep patterns, particularly in individuals with insomnia, jet lag, or shift work disruptions.
How Does Alcohol Affect Sleep?
While alcohol is often thought of as a relaxant that helps people fall asleep, it can actually disrupt the sleep cycle. Initially, alcohol can have a sedative effect, making it easier to fall asleep. However, as the body processes alcohol, its negative effects on sleep become evident. Alcohol interferes with the stages of deep sleep, particularly REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is essential for restorative rest.
People who consume alcohol before bed may experience fragmented sleep, waking up frequently throughout the night. This disruption reduces the overall quality of sleep, leaving individuals feeling tired and groggy the following day. Moreover, alcohol can lead to dehydration, which can cause a dry mouth, headaches, and other discomforts that may further interrupt sleep.
Interactions Between Melatonin and Alcohol
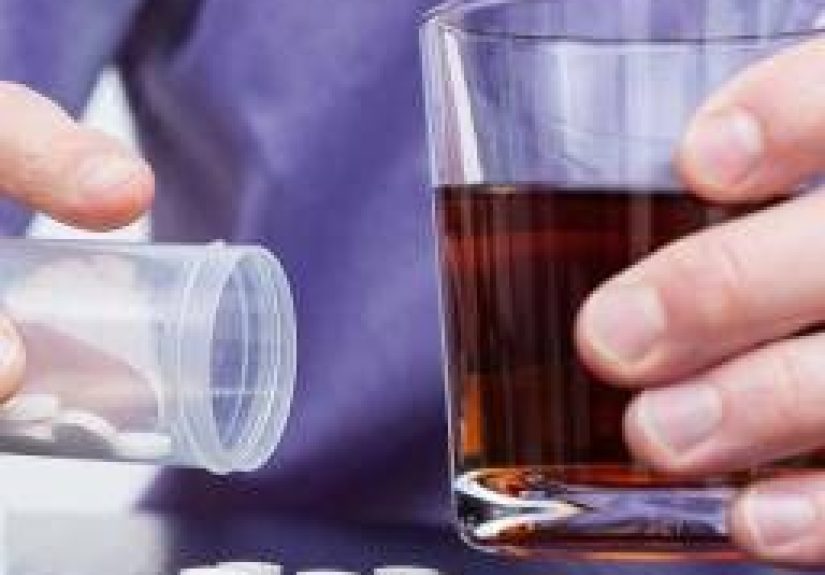
Now, let’s explore what happens when melatonin supplements are taken in conjunction with alcohol. While alcohol doesn’t directly interfere with melatonin production, its sedative effects can overlap with those of melatonin, potentially leading to increased drowsiness. In other words, both alcohol and melatonin work to induce sleepiness, but their combination can result in an overly sedative effect, leading to excessive drowsiness or grogginess upon waking.
There’s also evidence to suggest that alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to process melatonin efficiently. Alcohol is a known disruptor of sleep architecture, and when combined with melatonin supplements, it could potentially counteract melatonin’s sleep-regulating effects. This means that while melatonin might help initiate sleep, alcohol’s negative impact on sleep quality could prevent the restful, restorative sleep that melatonin normally promotes.
Potential Risks of Combining Melatonin and Alcohol
While the occasional combination of melatonin and alcohol is not likely to cause major harm, regular use of both can result in some undesirable effects. Combining alcohol with melatonin can amplify the sedative effects of both substances, leading to excessive drowsiness, dizziness, and difficulty waking up the next day. These effects could be especially dangerous when driving or performing tasks that require focus and attention.
In addition, the combination may worsen alcohol’s already disruptive effects on sleep, leading to more frequent waking and a lower quality of rest. For those who rely on alcohol to relax or sleep, adding melatonin might not be a reliable solution to improving sleep quality, and it may even exacerbate the issue.
The Benefits and Uses of Melatonin
Melatonin is commonly used as a sleep aid for people dealing with various sleep disorders. Some of the key benefits and uses of melatonin include:
- Improving sleep in people with insomnia: Melatonin can help people who struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, particularly if their sleep-wake cycles are out of sync.
- Managing jet lag: Melatonin is frequently used to help reset the body’s internal clock after crossing multiple time zones. Taking melatonin at the right time can minimize the symptoms of jet lag, such as fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and irritability.
- Assisting shift workers: For those who work irregular hours, melatonin supplements can help regulate sleep patterns and promote restful sleep during the day, despite nighttime work schedules.
- Potential benefits for mental health: Research suggests that melatonin may play a role in managing symptoms of depression and anxiety, as it has an impact on mood regulation and sleep.
Melatonin Dosage and Safety Considerations
The appropriate dosage of melatonin varies depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated. For most people, a low dose of 0.5 to 3 mg taken 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime is sufficient to improve sleep. However, higher doses may be required for certain sleep disorders or conditions like jet lag or shift work.
While melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using melatonin, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications. Overuse of melatonin can result in side effects such as dizziness, headaches, and morning grogginess.
Should You Combine Melatonin and Alcohol?
In conclusion, while melatonin and alcohol can both promote sleepiness, combining the two is not recommended due to the potential for excessive sedation and disruption of sleep quality. If you are using melatonin to manage sleep, it’s best to avoid alcohol close to bedtime. If you have already consumed alcohol and are considering melatonin as a sleep aid, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with this combination and monitor how your body reacts.
Ultimately, it is essential to prioritize healthy sleep habits, including managing alcohol intake and considering lifestyle changes that can improve your sleep without relying heavily on supplements.
Personal Experiences and Additional Considerations
Many people have shared their experiences regarding the combination of melatonin and alcohol. Some individuals report that they felt overly drowsy and struggled to wake up the next day after combining the two. Others have shared that while melatonin helped them fall asleep faster after drinking, they still experienced fragmented sleep and woke up feeling tired. For people with a history of alcohol dependence or those using alcohol to self-medicate for sleep issues, adding melatonin might not be the best solution. Instead, addressing the underlying sleep disorder or alcohol-related issues with professional help could provide more sustainable results.
If you’re considering using melatonin while managing alcohol consumption, it’s wise to start with small doses and monitor your body’s response. Every individual reacts differently to both substances, so paying attention to how they affect your overall well-being is crucial. Remember that the goal is to develop a healthy, sustainable sleep routine that doesn’t rely on combining sedatives like alcohol and melatonin.
Conclusion
Melatonin is a powerful hormone that serves many important functions in the body, primarily in regulating sleep. While alcohol may help you relax, it can interfere with the sleep benefits melatonin offers. When combined, the two substances can lead to excessive drowsiness, reduced sleep quality, and grogginess. To get the best results from melatonin, it’s important to maintain healthy sleep habits and avoid drinking alcohol close to bedtime. Always consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns about using melatonin, particularly in combination with other substances.
SEO Tags